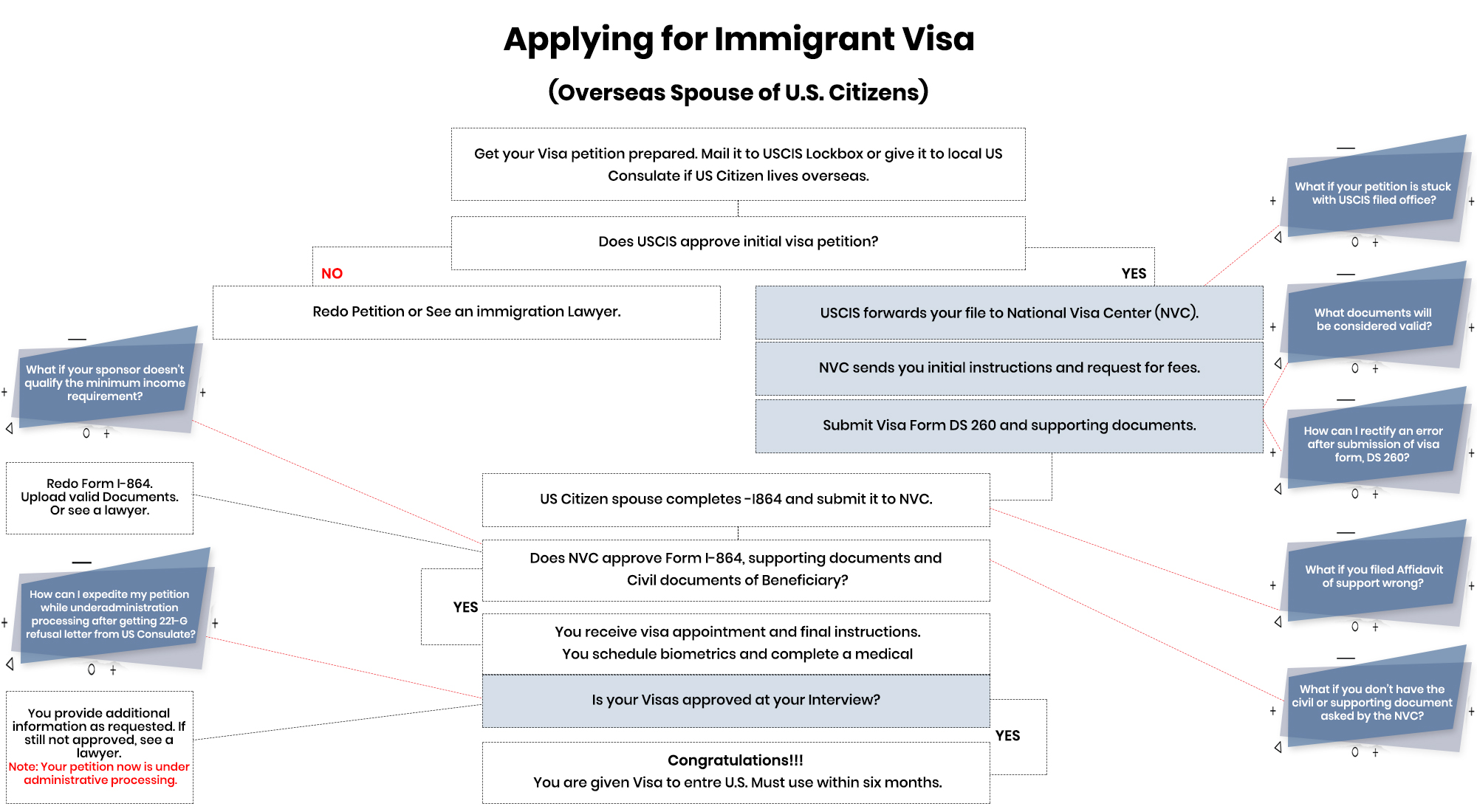
What is the difference between Tax Transcripts and 1040 Tax?
What is the difference between Tax Transcripts and 1040 Tax?
Tax Transcripts and Form 1040 are both related to income tax filings in the United States, but they serve different purposes and provide different types of information. Here’s a breakdown of the differences:
Tax Transcripts: A tax transcript is a document that provides a summary of information from a previously filed tax return. It is an official record of the taxpayer’s tax-related activities. There are different types of tax transcripts available, including:
- Return Transcript: This transcript shows most line items from a tax return as originally filed, including any accompanying forms and schedules.
- Account Transcript: This transcript provides information on the current status of the taxpayer’s account, including payments, penalties, and adjustments.
- Wage and Income Transcript: This transcript includes information on income reported to the IRS, such as W-2 forms, 1099 forms, and other income documents.
Tax transcripts are typically used for various purposes, such as verifying income for mortgage applications, student loan applications, and certain types of financial aid.
Form 1040: Form 1040 is the standard individual income tax return form used by taxpayers to report their income, deductions, credits, and calculate their tax liability for a specific tax year. It is the primary document that taxpayers fill out and submit to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) to report their annual income tax obligations.
Form 1040 requires taxpayers to provide detailed information about their income sources, deductions, credits, and tax liability calculations. It includes various schedules and forms that may be necessary depending on the individual’s financial situation.
In summary, a tax transcript is a summary of information from a previously filed tax return, while Form 1040 is the tax return form itself that taxpayers fill out to report their income, deductions, and tax liability. Tax transcripts are used for verification and reference purposes, while Form 1040 is the primary document submitted to the IRS for income tax purposes.
Why U.S. Consulate does asks for Tax Transcripts instead of 1040 Federal tax Forms?
The U.S. Consulate may request tax transcripts instead of Form 1040 federal tax forms for several reasons. Here are a few possible explanations:
Verification of Income: Tax transcripts provide a more comprehensive and official record of an individual’s income and tax-related activities. They include information on wages, income from investments, and other sources reported to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). Consulates may prefer tax transcripts to ensure the accuracy and authenticity of the income information provided by visa applicants.
Consistency and Verification: Tax transcripts allow consular officers to compare the income reported by visa applicants with the information provided on other supporting documents, such as bank statements or employment records. This helps verify the consistency and credibility of the income claimed during the visa application process.
Prevention of Fraud: Tax transcripts can help detect fraudulent activities or misrepresentation of income. They provide an additional layer of scrutiny and help ensure that applicants are providing accurate and reliable financial information.
Standardized Documentation: Consulates may request tax transcripts to maintain consistency and standardization in their documentation requirements. Tax transcripts are official documents issued by the IRS, providing a reliable and uniform source of income information for visa applicants.
It’s important to note that the specific requirements and preferences of each U.S. Consulate can vary. Therefore, it’s advisable to carefully review the consulate’s instructions and follow their guidelines regarding the submission of tax transcripts or other relevant documents.